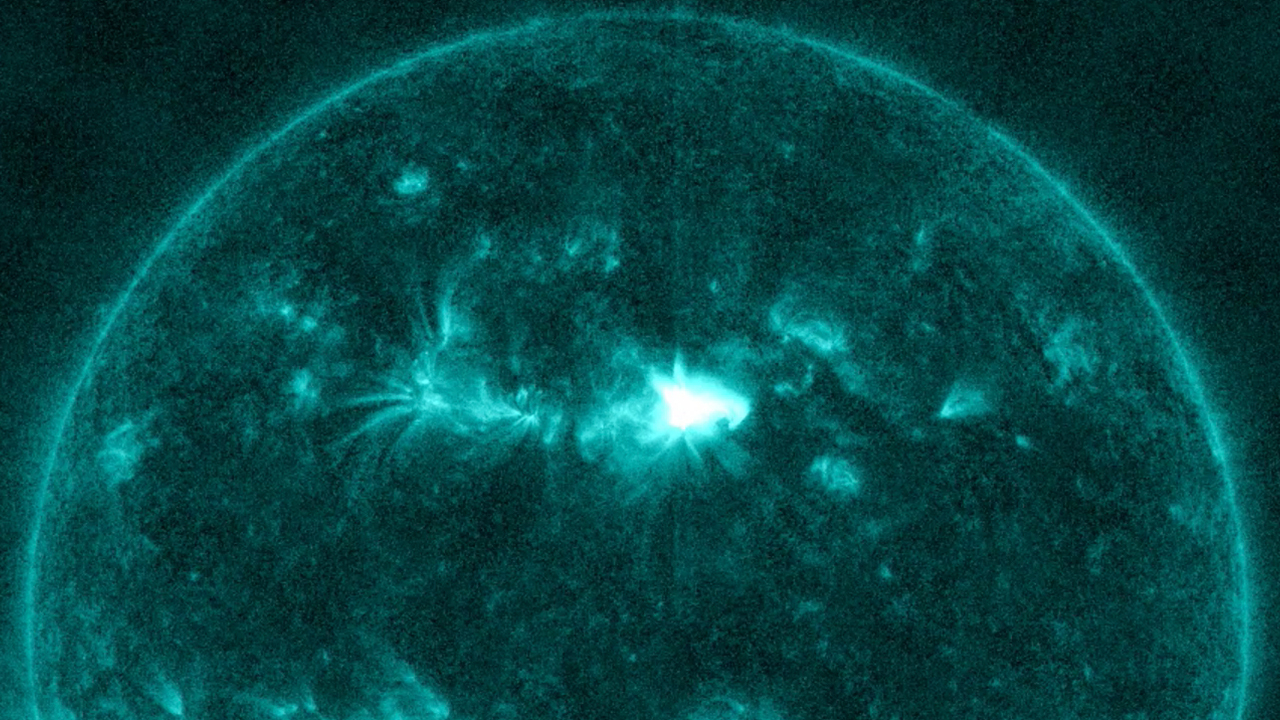
A sunspot that erupted quickly caused a huge flame to be released.
the outbreak the sun The activity, officially known as AR2975, released a strong Class X glow that was already causing a temporary blackout of shortwave radio signals in the Americas, according to the SpaceWeather.com . (AR2975 . has already been burped more than 17 Average glow for the past few days, but this explosion is a bit stronger.)
Pilots, navigators, and radio amateurs may have noticed unusual propagation effects at frequencies below 30 MHz. [megahertz]The site reported Wednesday (March 30) in the hours after the flash.
Related: The Earth is preparing for a possible solar storm and aurorae
Solar flares are categorized first by category – Category A being the weakest, then Category B, C and M, with Category X being the strongest – and then by size, with smaller numbers representing the brightest flares. Small within the class. Wednesday’s glow was an X1.3 class glow, according to SpaceWeather.
Flares are bursts of light, but are sometimes associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which shoot points of charged particles into space. If a coronal mass of glare is ejected and directed toward the ground, this may cause this to occur dusk It is the amazing light produced by the collision of charged particles in the Earth’s atmosphere. SpaceWeather added that there is circumstantial evidence that the CME appeared from the Sun, but more observations are needed to confirm this.
“It is almost certain that a CME missile exited from the site of the explosion,” he continued, noting that the US Air Force had spotted The second type of solar radio exploded which may be associated with shock waves from CME.
One of 17 different active AR 2975 sunspot glows illuminated in this image from NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory taken March 28-29, 2022. (Image credit: NASA)
Also, NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory sun tsunami picture It is clearly a result of the CME leaving the heliosphere,” added Space Weather.
SDO officially captured images of the event at 13:35 EDT (1835 GMT), but NASA did not provide detailed predictions beyond indicating the general risks that can occur with solar flares.
NASA officials wrote in a letter Confirm .
The sun began its current cycle of solar activity in 2019 and is expected to reach its peak around 2025. Scientists are still not sure how active this solar cycle is, although forecasts indicate fewer sunspots than usual.
NASA and other space agencies are constantly monitoring solar activity to improve solar weather forecasts. In most cases, CMEs simply cause dusk When charged particles collide with the Earth’s magnetic lines. However, it can cause stronger storms issues With satellites or power lines.
Follow Elizabeth Howell on Twitter Tweet embed . Follow us on Twitter Tweet embed or running Facebook .